The Ultimate Guide to Consulting Platforms



Consulting platforms connect businesses with qualified consultants for a wide range of needs, from short-term freelance support to full-time interim roles. These platforms can take many forms: established consulting firms that offer platform-enabled services, curated marketplaces such as Consultport or Comatch, or broad talent networks like Upwork that match clients with individual experts or smaller teams. With fast access to vetted specialists and more flexible resourcing models, consulting platforms are becoming an essential component of the modern consulting landscape.
Consulting platforms are online marketplaces connecting freelance consultants and clients. These platforms provide a space where businesses can find and book consultants and experts to provide support across specific industries and functions.
The rise of consulting platforms in the last decades shows a clear shift in the global workforce landscape. They have become essential, enabling companies to access a vast pool of talent worldwide.
Additionally, many leading organizations are finding it critical to access top-tier external consultants. As reported by Forbes, the recent trend of “quiet hiring” by companies is crucial for “acquiring new skills without actually hiring new full-time employees”, creating a blended workforce where “full-time permanent employees work side-by-side with freelancers”. McKinsey suggests that 25% of professionals prefer flexibility and independence of agile talents, estimating that 50% of the corporate workforce will be made up of full-time, regular employees.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of consulting platforms, answering these questions:
- Why are consulting platforms becoming essential for businesses?
- What are the main benefits of engaging with consulting platforms?
- How to engage with consulting platforms?
Types of Consulting Platforms
1. Marketplaces
Marketplaces act as open or curated digital environments where clients can post project requirements and consultants can apply or be matched to them. They typically support a wide range of industries and project types, from strategic consulting to operational roles.
Examples: Consultport, Comatch, consultingheads, Upwork.
2. Traditional Consulting Firms (Platform-Enabled Models)
Some large consulting firms now use platform-style components to deliver work more efficiently. These firms still employ their own consulting teams but leverage digital tools to manage talent, collaborate with clients, and scale resources on-demand.
Examples: Deloitte, PwC, EY, KPMG, Accenture, Boston Consulting Group, L.E.K. Consulting.
3. Specialized Platforms
Specialized platforms focus on a specific industry, function, or skill set. They match clients with experts who have deep knowledge in areas such as software consulting, digital marketing, project delivery, or niche technology stacks.
Examples: Consultport (digital, AI, marketing), monday.com (software consulting verticals), and other niche talent communities.
The Rise of Consulting Platforms
Freelance platforms have seen exponential growth in recent years. As of 2023, the freelance market is estimated to increase at a CAGR of 15% between 2022 and 2030, with up to 162 million freelancers in Europe and the United States, consisting of 20 to 30 percent of the working-age population. Moreover, 70% of freelancers report they find their clients through online freelance platforms, and only 11% rely on more traditional sources such as word of mouth and referrals. Considering management consultants only, 90% of corporate leaders have shown interest in hiring freelance consultants to move to hybrid staffing models featuring a flexible, blended workforce.
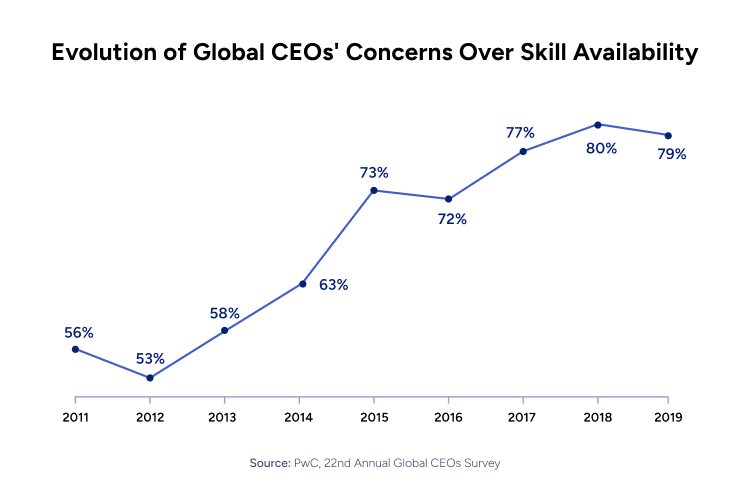
Freelance platforms offer a marketplace for businesses to browse profiles of freelancer consultants based on skills, experience, location, or other criteria. This can be a solution to the rising problem of talent gaps for companies. As per PwC, 79% of CEOs described talent gaps as a significant impediment to growth and performance, and “quiet hiring” is becoming a driving solution to this issue. A prime example of this situation is Google, which has more freelance workers (54%) than regular, full-time workers (46%).
By 2030, the freelance platform market is projected to reach $14.39 billion, driven by several key factors. According to Consultport’s “
The benefits of Consulting Platforms for Businesses
Cost efficiency. Hiring independent consultants through freelance platforms can be significantly more cost-effective than traditional employment, as businesses and traditional consultancies can save on benefits, office spaces and equipment, avoiding adding permanent headcounts. For instance, in 2019, 43% of global organizations have reported that hiring freelancers led to 20% cost savings compared to full-time employees.
- Flexibility: Consulting platforms allow companies to access experts exactly when they need them—whether for rapid project support, temporary leadership roles, or long-term interim engagements. This flexibility helps organizations scale up or down without committing to full-time hires.
- Access to Talent: Platforms provide immediate access to a global pool of vetted consultants with specialized expertise that many companies do not have in-house. This ensures faster project starts and better alignment between the consultant’s skills and the project requirements.
- Efficiency: By streamlining the process of finding, evaluating, and engaging consultants, platforms significantly reduce administrative overhead. Clients benefit from faster matching, simplified contracting, and built-in payment and communication tools.
Access to External Expertise. Freelance platforms provide access to a global pool of skilled professionals, particularly beneficial for niche projects requiring specialized expertise. In fact, 51% of all freelancers provide knowledge services such as computer programming, marketing, IT, and management consulting.
Flexibility and Agility. By hiring freelancers, businesses can quickly scale their workforce up or down based on project demands. Almost 78% of business leaders in the US said they are more likely to hire freelancers rather than full-time employees while economic conditions remain uncertain, citing flexibility as a key benefit.
Fast Access to Talents. Freelance platforms provide fast access to desired profiles. For instance, Consultport and Toptal ensure clients are matched with the right consultants within 48 hours. This speed of delivery is a game changer for companies, enabling them to quickly find and onboard the right freelancers for their most critical projects.
Consulting Platforms: How-to Guide
There are multiple ways a company can engage with freelance platforms, depending on the type of platform. At Consultport, the process is fast and effective, with three main steps:
Step 1: Define The Project Needs
The process starts with the client submitting the specific project requirements. These include:
- Type of support needed (Management Consultant, Project Manager or Interim Manager)
- Functional expertise of the consultant (Finance, Operation Excellence, Procurement, PMO, etc.);
- Industry expertise of the Consultant.
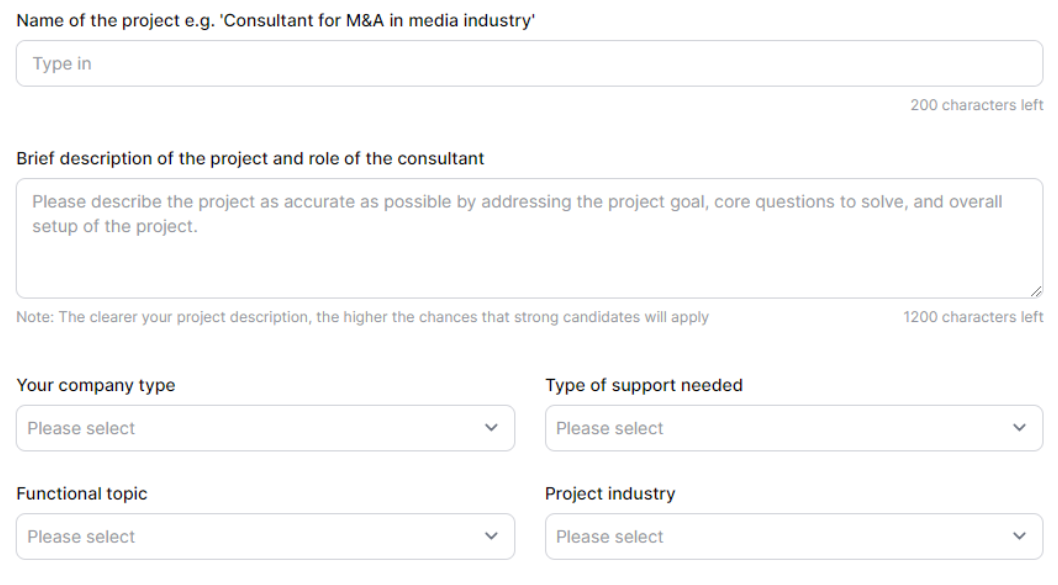
Moreover, the client also has the opportunity to indicate specific requirements related to the preferred way of work (hybrid/on site); the location; the way of consultant payment (daily rate or hourly rate); the maximum daily or hourly rate. Consultport also offers a set of pre-made templates that enables a faster way to submit a project request, The Lighthouse Guide.
After the client submits the first project brief, a project manager from Consultport will reach out and be dedicated to that project, making sure that 3 to 5 highly qualified profiles are proposed within 48 hours after the scoping of the project.
Step 2: Choose the Right Consultant
After the project submission, the best suited consultants are invited to the project and can pitch their expertise and motivation in 3-4 bullet points. Consultport reviews all pitches and presents only the best ones to the client. The client can interview as many consultants as they wish, including multiple rounds and onsite interviews, to ensure the best decision is made.
If the initial selection is insufficient, a second round of research can be launched to find the perfect candidate from Consultport's pool of 10,000 consultants. After a thorough analysis, the Project Manager submits a proposal suggesting the best candidates, and the client makes the final choice.

Do you want to know more? Discover Consultport’s Consultants.
Step 3: Start Working
After the client chooses the right consultant, Consultport project managers offer ongoing support before, during, and after projects. This extends to managing contracting and invoicing, allowing clients to focus on delivering high-quality work without the distraction of paperwork and logistics.
Moreover, all engagements are governed by strict contracts and confidentiality agreements, which helps in building trust and securing sensitive project information.
The Lighthouse Guide
The Lighthouse Guide by Consultport offers companies a streamlined way to submit project proposals with a simple, one-minute procedure. Utilizing pre-made templates based on previous successful projects, ensures that clients can quickly and easily articulate their project needs.
The first step is to provide the type of company, the industry, and a possible title of the project. Taking for example a carve-out project for PE companies:
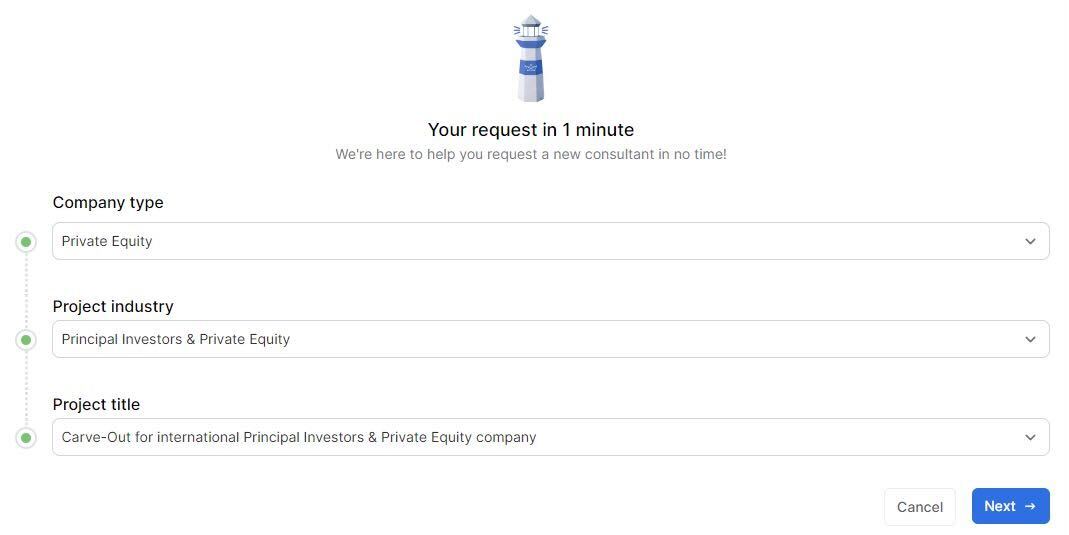
Based on previous projects, the fields will be automatically filled, and could be further customized:
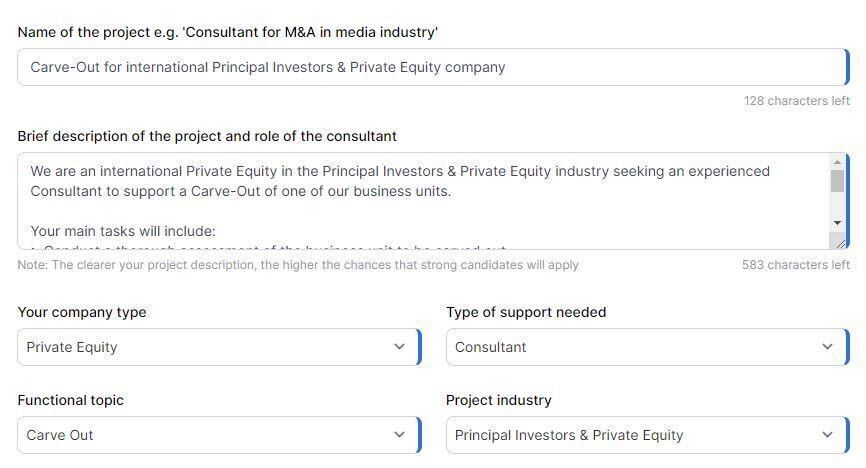
Also the consultant's requirements and the fields concerning the project duration and engagements will be presented, giving clients a benchmark of the length, cost, and consultant’s skills that led to a successful collaboration with a previous client.
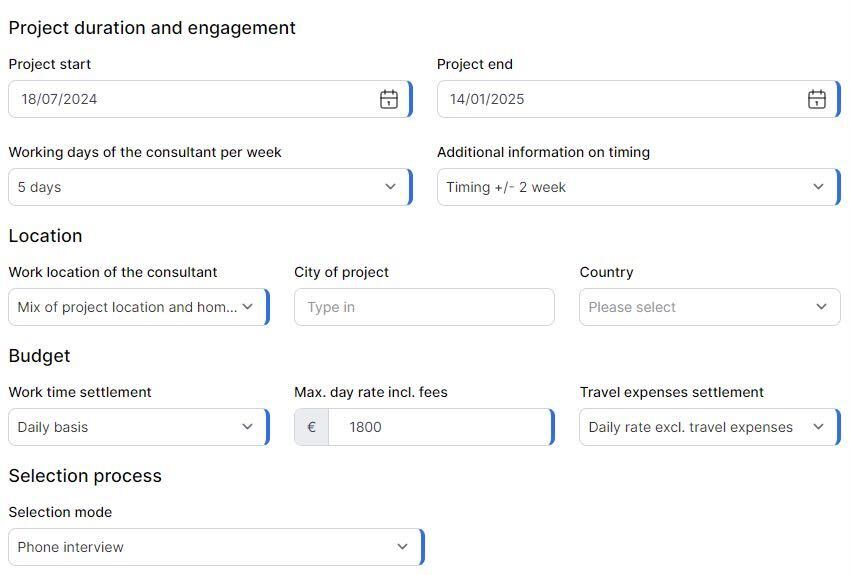
Thus, this powerful tool helps to clearly define project goals and requirements quickly, facilitating a smooth and effective engagement with experienced consultants and giving a benchmark of previous projects.
About Consultport
Consultport has a client-focused service to ensure clients will be matched with the right consultant, as fast as possible, and with a 360° quality management from onboarding to project implementation. Here are some reasons why clients should consider Consultport for their services:
Cost efficiency. Consultport’s platform offers access to top-tier consultants at a fraction of the cost of traditional consultancies, saving often up to 70% of the costs compared to traditional agencies or consultancies. This cost efficiency allows businesses to maintain high-quality consulting support while optimizing their budgets. To explore how much clients can save, visit Consultport’s Consulting Pricing Tool which compares the platform’s rates to traditional Consulting companies.
Quality and Speed: 71% of projects are staffed within 48 hours, ensuring that clients and consultants get timely support for projects.
Customized Service: Consultport offers a highly personalized consulting service, with project managers taking the time to understand each client's specific needs to provide the best match for their projects, with a 97% of client satisfaction score. For consultancies, this means getting support with proposals, covering topics outside their expertise and augmenting their workforce during peak times. For private equity firms, Consultport’s services provide crucial support on deals and help improve operational efficiencies.
Consultport helps freelance consultants maximize their potential, secure high-value projects, and build a robust professional network, while clients benefit from fast, reliable access to top-tier consulting expertise.
Ready to find the right consultant for your needs? Find a consultant
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Consulting Platforms & Related Resources
What are the main benefits of consulting platforms?
The main benefits are:
- Cost efficiency, as can save businesses over 20% in labor costs by reducing expenses related to benefits, office space, and equipment.
- Access to External Expertise, as freelance platforms provide access to a global pool of carefully selected talents who can provide highly qualified service, overcoming selection bias.
- Flexibility and agility: businesses can quickly scale their workforce up or down based on project demands. Almost 80% of employers plan to increase their use of freelancers, citing flexibility as a key benefit.
- Fast Process: In Consulting Platforms such as Consultport, the projects are staffed within 48 hours, enabling companies to quickly find and onboard the right freelance for projects.
How do consulting platforms ensure the quality of freelancers?
Consulting platforms typically offer reviews, references, and portfolios for freelancers. They also provide mechanisms for monitoring freelancers' work during projects and offer feedback to ensure quality standards are met.
Companies like Consultport ensures the high quality of freelancers by a strict selection process, with an initial background check and interviews to consultants.
What types of projects can consulting platforms support?
Consulting platforms like Consultport can support a wide range of projects, including management consulting, project management, interim management, financial planning, operations excellence, procurement, and more.
How do I request a consultant for my business?
Firstly, fill in Consultport’s short form indicating your contact details and consultant’s need. Once sent out, a project manager from Consultport will get back to you within the day to clarify the remaining questions before starting the matching process. In the following 48 hours, 4 to 5 profiles will be presented to you in form of a pitch through Consultport’s platform, and you can select which one you would like to interview.
Related Resources
- Best freelance platforms 2025: A market scan to help you shortlist options.
- How to hire and manage freelance consultants: Practical steps from sourcing to delivery.
- Consulting platforms guide (2025): Procurement-focused comparison and controls.
- Workforce Trend Report 2025:Understand how automation, remote work, and evolving employee expectations are shaping the future of work.
Conclusion
Consulting platforms have revolutionized the way businesses access talent, offering numerous benefits such as cost efficiency, flexibility, and fast access to highly skilled professionals. By leveraging these platforms, companies can bridge resource gaps, prepare for strategic events, and enhance their financial operations.
Consultport, with its streamlined process and commitment to quality, stands out as a leading consulting platform, ensuring that clients are matched with the right consultants quickly and efficiently. Whether you are a large corporation or an SME, consulting platforms can provide the expertise and agility needed to navigate today’s dynamic business environment.
on a weekly basis.


